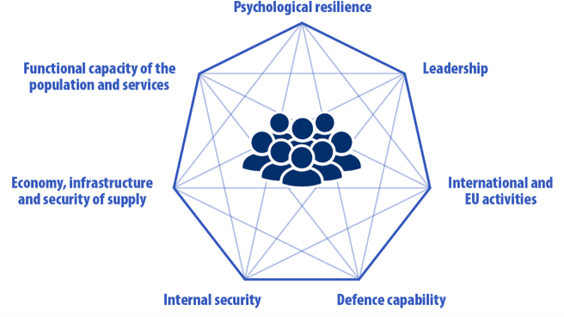
Vital functions of Society
The vital functions of society are essential for the functioning of society and must be maintained in all situations. The functions are highly interdependent. The vital functions of society form the basis of implementing comprehensive security. They serve as the foundation for planning practical tasks and responsibilities based on risk assessment. The vital functions of society are:
-
- Leadership
- International and EU activities
- Defence capability
- Internal security
- Economy, infrastructure and security of supply
- Functional capacity of the population and services
- Psychological resilience.
The vital functions of society are depicted in the shape of a diamond. The shape illustrates the interconnections and strong interdependencies between the vital functions. In the centre of the diamond the important role of individuals for the security of society is highlighted.
Leadership
Leadership is a function that enables actors to effectively coordinate and implement measures related to preparedness and response. Leadership capability must be secured in all situations and at all levels of operation. Effective management of disruptions and crises requires clarity in leadership. Clear leadership requires coordinated and consistent situational awareness, planning, organisation, decision-making, implementation and assessment.
International and EU activities
Building security is a cross-border activity. Finland operates in a networked world in which security measures are also inevitably intertwined with a broader international context. Vital functions are also influenced from outside of our country, and our own security situation is reflected in Finland’s external security. The European Union is Finland’s most important political and economic frame of reference and community of values. After becoming a NATO member, Finland is part of a military alliance. The membership strengthens the security of Finland, Europe and the Alliance as a whole. When it comes to supporting European security, NATO’s and the EU’s roles complement and strengthen each other.
Defence capability
The goal of maintaining defence capability is to deter the use of military force and the threat thereof. If necessary, military threats against Finland will be countered by using military force jointly with NATO allies. Deterrence encompasses preparedness and other activities by society as a whole, as well as communication about them. NATO membership and international defence cooperation strengthen Finland’s defence capability. Finland engages in defence cooperation on the basis of its own premises and common interests.
Internal security
Internal security refers to the capability to prevent criminal activities, accidents, environmental damage and other similar threats targeting Finland and its population, as well as to manage their consequences. Internal security is a state in which people can enjoy the rights and freedoms guaranteed by the legal system without fear or insecurity caused by criminal activities, disruptions, accidents, and other equivalent national and international phenomena.
Economy, infrastructure and security of supply
Securing the functioning of the economy, infrastructure and security of supply provides the funding and other resources necessary to maintain vital functions. Measures are taken to secure the domestic and international infrastructure, organisations, structures, services and processes essential for vital functions.
Functional capacity of the population and services
Individuals capable of functioning are the prerequisite of a functioning of society. Functional capacity encompasses the physical, psychological, social and ethical elements. The population’s functional capacity and wellbeing are secured by maintaining the central basic services, which promote the population’s ability to cope independently in all circumstances.
Psychological resilience
Psychological resilience refers to the ability of individuals, communities and society to withstand the stress caused by crisis situations and to recover from their impacts. The foundation for psychological resilience is created in normal conditions, and it plays a key role in the maintenance of functional capacity during crisis. Good psychological resilience promotes recovery from crises.
